Decentralised Identity (DID)
Decentralised Identity (DID) is a framework for creating self-sovereign identities on blockchain networks without reliance on centralized authorities.
What is DID?
A Decentralised Identity is a digital identity that is:
- User-Controlled: You own and manage your identity directly without intermediaries
- Portable: Your identity works across multiple platforms, services, and blockchain networks
- Verifiable: Your identity can be cryptographically verified by others
- Privacy-Preserving: You control what information is revealed and to whom
- Persistent: Your identity persists even if a single service goes down
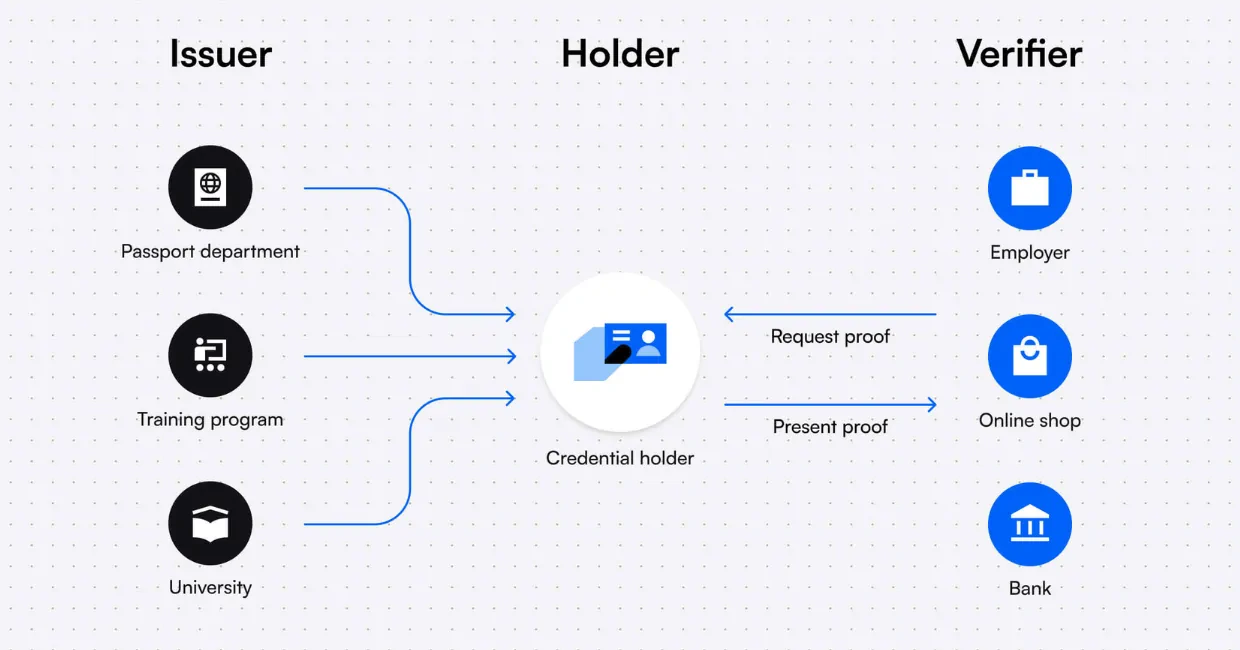
DID Standards
W3C DID Specification
The W3C (World Wide Web Consortium) defines a standard format for DIDs:
did:method:method-specific-idExample:
did:eth:0x1234567890123456789012345678901234567890Where:
did- Scheme identifiereth- Method (Ethereum-based)0x1234...- Method-specific identifier (Ethereum address)
How ERC-7866 Enables DID
ERC-7866 implements a practical DID system for Ethereum by providing:
1. Human-Readable Identifiers
Instead of raw wallet addresses, users claim memorable usernames:
alice@eth.soul
bob@polygon.soul2. Cryptographic Verification
Usernames are tied to wallet addresses, creating a verifiable on-chain identity:
- Username → Address mapping
- Address → Profile data retrieval
- Signature verification for ownership
3. Cross-Chain Portability
The same username format works across all EVM chains:
alice@eth.soulon Ethereumalice@polygon.soulon Polygonalice@arb.soulon Arbitrum
All pointing to the same user with consistent identity.
4. Privacy Control
Users control visibility of their profile data:
- Public profiles accessible to everyone
- Private profiles hidden from unauthorized access
- Selective disclosure of information
DID Use Cases
Professional Identity
Maintain separate identities for work and personal life:
- Work profile: Professional credentials, portfolio
- Personal profile: Social presence, gaming avatars
Reputation Systems
Build verifiable reputation across platforms:
- DeFi lending: Credit history tied to on-chain identity
- Gaming: Achievement and rank tied to gaming profile
- DAO governance: Voting history tied to member identity
Social Discovery
Find and connect with users:
- Search by username instead of address
- Discover users by avatar or profile info
- Build social networks around on-chain identity
Service Access Control
Grant access based on verified identity:
- NFT drops to specific usernames
- Whitelist addresses by identity
- Permission-based access to services
DID vs. Web2 Identity
| Aspect | Web2 | DID (ERC-7866) |
|---|---|---|
| Control | Centralized platform | User-owned |
| Portability | Platform-specific | Cross-platform |
| Verification | Email, phone | Cryptographic |
| Privacy | Platform-managed | User-controlled |
| Censorship | Platform can revoke | Blockchain immutable |
| Cost | Free (but your data is product) | Small on-chain cost |
DID Architecture with ERC-7866
The diagram illustrates how ERC-7866 enables decentralised identity:
- User Claims Username → Creates on-chain identity
- Sets Profile Data → Avatar, bio, metadata (on IPFS/Arweave)
- Creates dApp Avatars → Different identities per application
- Other Users Verify → Query on-chain profile by username or address
- Services Integrate → Games, DAOs, DeFi can use identity
Security Considerations
Non-Transferability
Usernames are soul-bound to addresses:
- Cannot be sold or transferred
- Prevents identity hijacking
- Ensures persistent reputation
Immutable Records
Once created, profile history is permanent:
- Cannot erase past actions
- Promotes accountability
- Enables trustworthy reputation
On-Chain Proof
All identity claims are cryptographically verified:
- No fake identities
- Proof of ownership via signature
- Verifiable by smart contracts
Privacy in DID
ERC-7866 balances transparency with privacy:
Public Avatars
Visible to all users:
- Professional profiles
- Gaming achievements
- Social identities
Private Avatars
Hidden from public view:
- Sensitive information
- Context-specific data
- Personal preferences
Selective Disclosure
You control what's revealed:
- Show profile to specific addresses
- Time-limited access
- Conditional disclosure
Future of DID
Cross-Chain Identity
- Unified identity across all blockchains
- Interoperable DID standards
- Multi-chain reputation systems
Privacy Enhancements
- Zero-knowledge proofs for selective disclosure
- Anonymous credentials
- Privacy-preserving verification
Integration with Web3
- Wallet connections using DID
- Decentralized authentication
- Identity-based access control
Getting Started
To implement DID using ERC-7866:
- Deploy SoulProfile contract on your target chain
- Create a profile with your chosen username
- Set avatars for different applications
- Share your username with others
- Integrate into your service to verify user identities
See the Implementation Guide for code examples.