
Beyond Blockchain - An Introduction to Tangle
Overview
What to expect from this session
- Problems with current world
- Bitcoin and Blockchain
- Problems with Blockchain
- What is Tangle
- Blockchain vs Tangle
- Use-cases and Implementations
Problem
- Huge fees for money/asset transfer.
- Delayed oversees transfer.
- Controlled by any government or Institution.
- Corrupt Humans. No Trust among peers.
Solution
Blockchain
- Bitcoin for the first time established trust in a trustless system.
- Blockchain paved the way to more distributed data systems.
- Peer to peer networks gave control back to the people who earlier felt at mercy of the big organisations.
- Internet faced a revolution unlike any other.
- Everyone can now be rewarded for every little action they do. Incentives are the new have-to and not can do.
- Bitcoin for the first time established trust in a trustless system.
- Blockchain paved the way to more distributed data systems.
- Peer to peer networks gave control back to the people who earlier felt at mercy of the big organisations.
- Internet faced a revolution unlike any other.
- Everyone can now be rewarded for every little action they do. Incentives are the new have-to and not can do.
A Blockchain World









![]()








![]()
![]()
![]()

Problems with Blockchain
- Users vs Network
- Scalability
- Tax/ Miners
- Always Online
- High end hardware requirements
Solutions in Blockchain
- Users vs Network - Solved by various consensus mechanisms
- Scalability - Solved temporarily by lightning network, raiden network, plasma, sharding, etc.
- Tax/ Miners - No solution
- Always Online - No solution
- High end hardware requirements - Light chains solve to some extent if mining is not involved.
Tangle
 It is a novel new distributed ledger architecture that is based on a DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph). One might refer to it as a "Blockchain without Blocks and the Chain" (semantically, it's not really a Blockchain).
It is a novel new distributed ledger architecture that is based on a DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph). One might refer to it as a "Blockchain without Blocks and the Chain" (semantically, it's not really a Blockchain).
IOTA Whitepaper
At its core, the Tangle still has the same underlying principles as a Blockchain: it's still a distributed database, it's still a P2P Network and it still relies on a consensus and validation mechanism.
Directed Acyclic Graph ( DAG )
In mathematics and computer science, a directed acyclic graph (DAG), is a finite directed graph with no directed cycles.Adding a transaction
Another Transaction
New Tangle State
Confirmation Levels
Propagation Delay
Double Spend
Double Spend Resolution
Offline Tangle
Scaling in Tangle
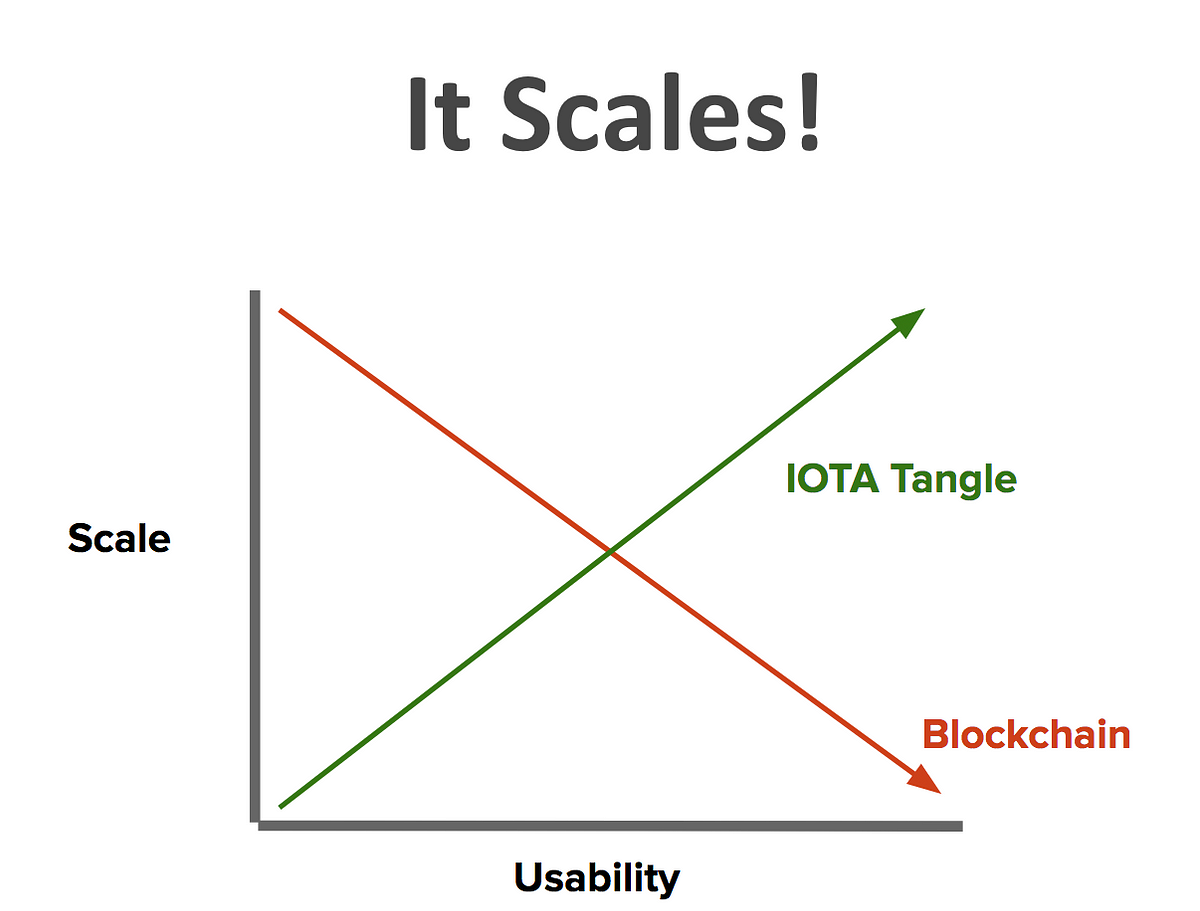
Blockchain vs Tangle
| Blockchain | Tangle |
|---|---|
| Linked list | Graph |
| Transactions are grouped in blocks and blocks are validated. | Transactions validate two other transaction. |
| Network requires certain fee for transaction | No Transaction Fee |
| Sequential Consensus | Parallel Consensus |
| Network gets slower as nodes increases. | Network gets faster as nodes increases. Infinitely Scalable. |
| Always Onchain | Offchain onchain anytime. Partioning. |
Use-Cases




Implementations
Summary
Few key Take-Aways
- We are already living in a world where blockchain is slowing sweeping into our daily lives slowly.
- Blockchain has it's own flaws which Tangle overcomes.
- Spectre, Hashgraph are also trying to do similar to what Tangle is doing.
- IOTA establishes a perfect platform for machine economy to rise.

Questions?
Kumar Anirudha : https://anirudha.dev
Twitter: @kranirudha
Github: @anistark
Mail: mail@anirudha.org












